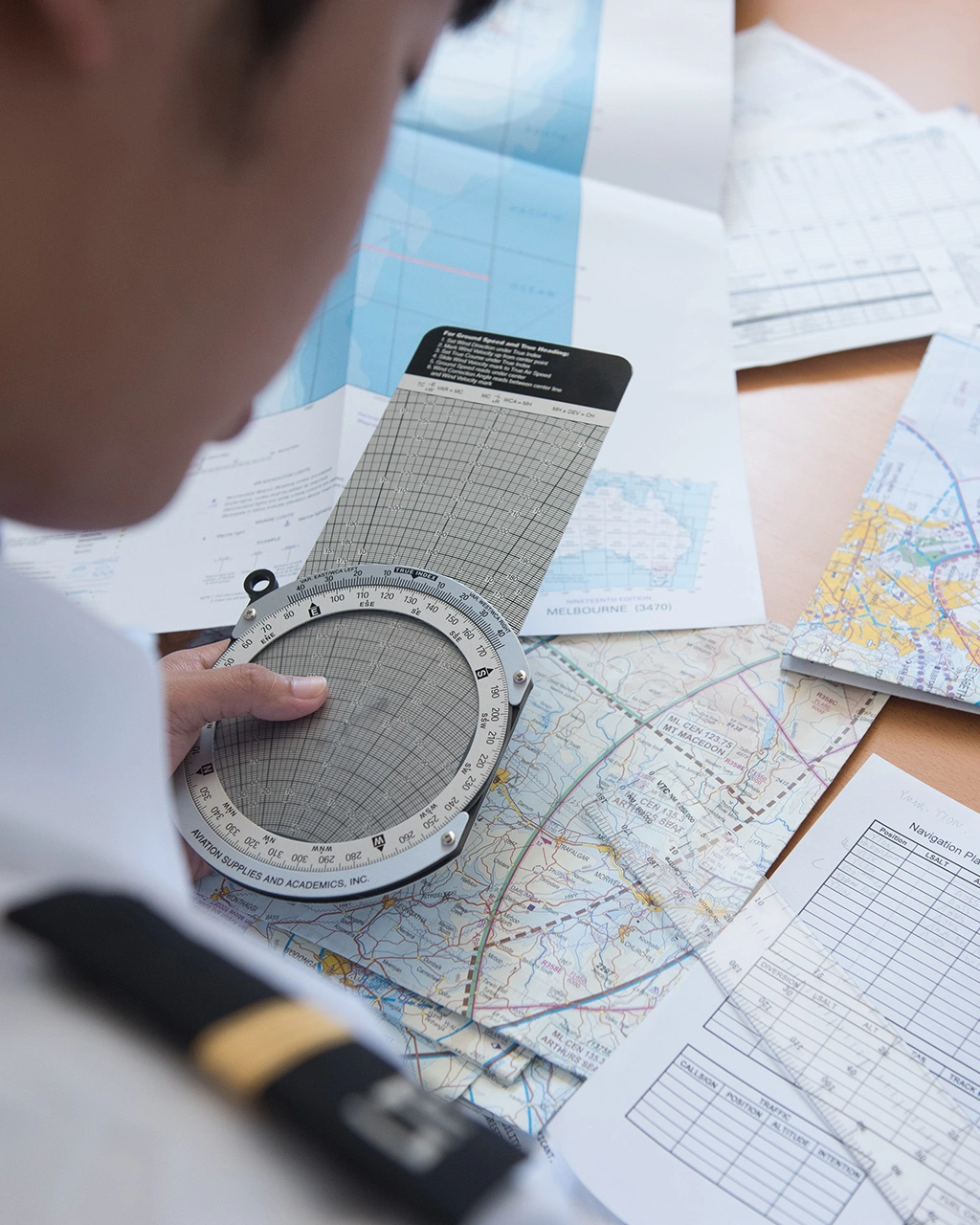
What are some tips for successful flights? Our instructors are a wealth of knowledge, so we asked them for their best pilot flying tips!
Across Australia and around the world, thousands of recreational and commercial pilots complete successful flights with accidents thankfully being rare. When accidents do occur, investigations often reveal that standard processes and simple practices weren’t carried out. In aviation, this is known as “human factors”.
There’s a lot to take in when you are learning how to fly, and sometimes the most simple of advice can help to make your flying safer and more enjoyable. So, here are some pilot flying tips from our experienced LTF flight instructor team!
Planning
Prior planning prevents poor performance. Adages like these become cliche for a reason. Have a thorough flight plan. Know your radio calls and frequencies, the landing airport layout, to making sure you ate recently, (take snacks and water, always) and are well-rested before take off.
Other essential planning tips for a successful flight include:
– Knowing the current weather and forecast on the route and at aerodromes
– Being aware of the aerodrome conditions and aircraft suitability
– Knowing ATC rules and procedures for that flight and NOTAMs

Familiar Territory
Flying can throw enough curveballs at a pilot without creating additional ones through oversight and inexperience. Recognisable and accustomed situations are ways of further minimising risk and avoiding threat situations.
Some examples of what we mean by that:
– Flying in a new aircraft? Fly it in good conditions and in a familiar place.
– Pick the best day to head to a new destination.
No matter how long you have been flying, one of the best pilot flying tips is to carry out one cockpit task at a time. Multitasking means spreading your attention thinly and potentially missing something. Another one of our pilot flying tips is that even if you have been in an emergency and survived (high five by the way), practice your emergency procedures.
Not Flying is OK!
It’s OK to decide not to fly when things happen like a change in weather, you forgot something or are running late. We know how much you want to get up there, but you can choose to fly another day if things aren’t aligning and subsequently putting pressure on your flight plan.
Good piloting comes from an honest assessment of all the factors that enable the safest flight experience. If you decide to push ahead, keep a cool head in situations like if the aerodrome is busy, and don’t succumb to passenger pressure or your own get-there-itis.
Know the Rules
Non-compliance is a contributing factor to many accidents, particularly fatal ones. Whether it is validity, memberships, operating in VMC conditions or one of the abundance of rules and regulations, they play heavily in tips for successful flights.
Being compliant is pivotal to safety, and the rules and regulations have come about not just from the fatal mistakes of past pilots but because our skies are increasingly busy with aircraft.
Brief Your Passengers
Whilst you’re the one behind the controls, an important pilot flying tip is to brief your passengers even if they are friends or family who fly with you regularly and in the same or similar aircraft. It’s good practice to always run through:
– No smoking in or near the aircraft
– Seatbelt adjustments
– Emergency procedure including life jacket and emergency equipment location
– Stowage of luggage and personal items.
Tell your passengers always to let you know if they aren’t feeling well, if they notice something with the aircraft or have questions during the flight. Check in with them throughout the trip (even short ones).
Evaluate and Improve
Being in the sky is one of the most vulnerable places on Earth. Very experienced pilots have failed before as frequently as novices. Experience can be your greatest asset or your blind spot by way of complacency or worse, cockiness. Soar to great heights but keep your ego grounded on terra firma.
Evaluate after every flight. You should be looking to improve something every flight. Professionals across all sectors, through to elite athletes all look at their last performance and see what can be improved.
Never stop learning. Write your own notes and study them. Doing a flight check with someone different every year is a great habit to get into in between your biennial flight reviews.
You can get more pilot flying tips by subscribing to our YouTube channel. We have RPL/PPL flying lessons, aircraft pre-flight check videos, and more. Click the button below to subscribe!
Chat to one of our flight training specialists to get your pilot training off the ground. Email hello@learntofly.edu.au or go to https://drift.me/learntofly/meeting to book a meeting and school tour.